Bike reflectors are passive safety devices that bounce back light from car headlights or streetlights, making cyclists visible in low-light or nighttime conditions without needing a power source. Their role is essential for road safety and accident prevention, as they improve visibility from multiple angles. The history of bike reflectors dates back to the early 20th century, when glass bead and prismatic technology were first applied to bicycles, later evolving into plastic, LED-enhanced, and high-intensity retroreflective designs. Cyclists need them to comply with safety laws, visibility standards, and commuting requirements, yet many face difficulty choosing the right reflector due to variations in mounting position, brightness, durability, and compatibility with modern bike designs. In essence, bike reflectors are not just accessories but critical visibility tools that provide long-term value in terms of safety, compliance, and rider confidence.
This article explains what a bike reflector is, explores the different types available, and offers guidance on how to choose the right one for safe and effective cycling.
Table of Contents
What is a bike reflector?
A bike reflector is a passive visibility device that uses retroreflective materials, such as prisms or microbeads, to bounce incoming light (like car headlights) back toward its source, making the cyclist visible at night or in low-light conditions. The first practical bicycle reflectors appeared in the early 20th century in Europe and the U.S., developed by safety equipment manufacturers who adapted road reflector technology to bicycles. Over time, designs evolved from glass and metal reflectors to modern plastic, high-intensity, and integrated LED-enhanced versions, improving durability and brightness. Many local laws, such as those in the U.S., EU, and Japan, require bikes sold to have reflectors on the front, rear, pedals, and wheels, ensuring a baseline level of nighttime safety. A bike reflector today is not only a regulatory requirement but also a critical safety feature, valued for its ability to reduce accidents and increase rider visibility without consuming power.
How do bicycle reflectors work?
Bicycle reflectors work by using retroreflection technology, where specially designed surfaces made of microprisms or glass beads return incoming light—such as car headlights—directly back toward the source, making the cyclist appear brighter to drivers in low-light conditions. The mechanism is passive, meaning it requires no batteries or power, and reflectors are strategically placed on the front (white), rear (red), wheels (amber/white), and pedals (amber) to provide 360-degree visibility. This design ensures that cyclists are seen from multiple angles, enhancing road safety, compliance with traffic laws, and rider confidence during nighttime or poor visibility riding.
How important are reflectors on bicycles?
Reflectors are very important on bicycles because they significantly increase a rider’s visibility in low-light or nighttime conditions, reducing the risk of collisions with vehicles. They work passively without requiring power, ensuring that even if bike lights fail, the cyclist remains detectable. Related terms include retroreflection, visibility standards, traffic safety, accident prevention, and legal compliance, as many regions legally require reflectors on front, rear, pedals, and wheels. The value lies in providing a cost-effective, maintenance-free safety feature that enhances rider protection, driver awareness, and overall cycling safety on roads and trails.
When were bicycle reflectors invented?
Bicycle reflectors were invented in the early 20th century, when safety innovators in Europe and the United States adapted roadside glass-bead and prismatic reflectors for bicycles to improve nighttime visibility. Companies like 3M in the U.S. (founded 1902) played a major role in developing retroreflective technology, which was soon applied to bicycles through metal-framed glass reflectors mounted on the rear. Over time, the design evolved into lightweight plastic and prismatic versions, making reflectors affordable, durable, and later required by law in many countries as standard bicycle safety equipment.
Is a bicycle reflector luminous or non-luminous?
A bicycle reflector is non-luminous because it does not produce its own light but instead uses retroreflection to bounce external light, such as from car headlights, back toward its source. This makes the cyclist visible in low-light conditions without requiring batteries or electricity. Related terms include passive safety device, retroreflective prism, visibility aid, and non-luminous object. The value is that reflectors provide reliable, maintenance-free visibility even when active lighting is not available.
What is a bike reflector made of?
A bike reflector is typically made of plastic, glass beads, acrylic, polycarbonate, aluminum, and reflective coatings, because these materials provide the right mix of durability, clarity, light reflection, and weather resistance. Each material contributes to how effectively the reflector increases visibility and withstands cycling conditions.
- Plastic: Forms the outer casing, keeping the reflector lightweight and weatherproof.
- Glass beads: Embedded in older reflectors to create retroreflection by bending and returning light.
- Acrylic: Used in lenses for clarity and resistance to scratches while being lighter than glass.
- Polycarbonate: Adds strength and shatter-resistance for modern reflectors, ideal for rough riding conditions.
- Aluminum: Sometimes used in backing plates or mounts to provide rigidity and secure attachment.
- Reflective coatings: Applied to enhance brightness and efficiency by maximizing light return.
How is a bike reflector made?
A bike reflector is made through steps including design, material selection, molding, reflector surface creation, assembly, quality testing, and packaging, because each stage ensures the reflector is durable, weather-resistant, and capable of returning light effectively for rider safety.
- Design: Engineers create the shape, size, and prismatic pattern to optimize retroreflection.
- Material selection: Durable plastics, acrylic, or polycarbonate are chosen for clarity and impact resistance.
- Molding: The housing and lens are injection-molded to form the reflector’s structure.
- Reflector surface creation: Microprisms or glass beads are embedded or etched into the lens to bounce light back to its source.
- Assembly: The lens, housing, and mounting hardware are combined into a complete unit.
- Quality testing: Reflectors are checked for brightness, weather durability, and compliance with safety regulations.
- Packaging: Finished reflectors are labeled and prepared for sale as individual pieces or with bike kits.
What are the different types of bike reflectors?
Bike reflector types can be classified by location on the bike, design, and color, because these categories determine how effectively they enhance visibility and comply with safety regulations. Location ensures 360-degree coverage (front, rear, wheel, pedal), design influences durability and mounting style, and color follows legal standards to help drivers instantly recognize direction. Together, these types provide cyclists with passive, power-free safety across all riding environments.
Bike reflector types based on the location of the bike
Bike reflector types based on location include spoke reflectors, rim reflectors, wheel reflectors, rear reflectors, front reflectors, pedal reflectors, seat reflectors, frame reflectors, handlebar reflectors, and helmet reflectors, because each position improves visibility from different angles and ensures riders are seen in traffic. These placements work together to provide 360-degree safety coverage without requiring power.
- Bicycle spoke reflectors: Mounted between wheel spokes, they create side visibility while the wheel rotates.
- Bicycle rim reflectors: Attached directly to the rim, providing continuous reflective visibility along the wheel’s edge.
- Bicycle wheel reflectors: Larger versions placed on wheels to increase side and rotational visibility.
- Bicycle rear reflector: Mounted under the saddle or on the seat post, red in color to signal traffic behind.
- Bicycle front reflector: White reflector on the handlebar or fork, making the rider visible to oncoming traffic.
- Bicycle pedal reflectors: Amber reflectors on both sides of the pedals, increasing motion-based visibility.
- Bicycle seat reflector: Additional rear-facing reflector attached under or behind the saddle.
- Bicycle frame reflectors: Placed on the down tube or seat tube to enhance side and frontal visibility.
- Bicycle handlebar reflector: Mounted on the bar ends to increase visibility from the front and sides.
- Bicycle helmet reflectors: Reflective patches or clip-on reflectors improve head-level visibility.
Bike reflector types based on design
Bike reflector types based on design include standard reflectors, reflective tape, reflective bands, reflector lights, and wheel flash reflectors. Each design serves a different purpose in balancing visibility, convenience, and compliance with safety needs. These variations allow cyclists to choose between permanent fixtures, flexible add-ons, or combined active-passive systems for maximum visibility.
- Reflector: Traditional mounted units on the bike frame, wheels, or pedals that passively bounce back light.
- Tape: Adhesive reflective strips applied to frames, rims, or helmets for customizable and lightweight visibility.
- Band: Wearable reflective straps placed on arms, ankles, or backpacks to increase moving visibility.
- Light: Combination units with LEDs and reflective surfaces, offering both active and passive illumination.
- Wheel flash: Spoke-mounted or rim-mounted devices that create a circular reflective flash as the wheel spins.
Bike reflector types based on color
Bike reflector types based on color include yellow, white, and red reflectors, because each color is standardized for specific positions on the bike to help drivers quickly recognize direction and improve overall road safety. These color codes follow traffic regulations to ensure consistency and visibility.
- Yellow reflector: Commonly used on pedals, wheels, or sides to enhance lateral visibility in traffic.
- White reflector: Mounted at the front of the bike to make the rider visible to oncoming vehicles.
- Red reflector: Placed at the rear of the bike to signal following traffic, similar to car tail lights.
How do you choose a bike reflector?
You can choose a bike reflector by considering factors such as brand, price, material, durability, brightness, color, mounting position, compatibility, and legal compliance, because each element affects visibility, safety, and ease of use. These factors ensure the reflector provides reliable performance and meets riding conditions.
- Brand: Trusted manufacturers often meet safety standards and provide higher-quality reflectors.
- Price: Reflectors range from budget plastic units to premium multi-surface or LED-enhanced options.
- Material: Acrylic and polycarbonate offer better clarity and durability than basic plastics.
- Durability: Weather-resistant and shatter-proof reflectors last longer in varied riding conditions.
- Brightness: High-quality prisms or coatings increase retroreflective efficiency for better visibility.
- Color: White, red, and yellow reflectors must be used in their correct positions for safety and compliance.
- Mounting position: Front, rear, pedal, and wheel placements determine 360-degree coverage.
- Compatibility: Ensures the reflector fits your bike’s frame, wheels, or accessories properly.
- Legal compliance: Many regions require specific reflector types and placements to meet road safety laws.
How far away should bicycle reflectors be seen?
Bicycle reflectors should be seen from at least 150 meters (about 500 feet) away, because this gives motorists enough reaction time to identify and avoid cyclists in low-light conditions.
How far away should bicycle frame reflectors be seen?
Bicycle frame reflectors should be visible from 100–150 meters (330–500 feet), since they are fixed and provide front, rear, or side visibility depending on placement.
How far away should bicycle wheel reflectors be seen?
Bicycle wheel reflectors should be seen from 100 meters (about 330 feet), because their rotation creates motion visibility, helping drivers notice the cyclist from the side.
How far away should bicycle pedal reflectors be seen?
Bicycle pedal reflectors should be visible from 150–200 meters (500–650 feet), since the up-and-down motion of reflective pedals catches attention more effectively and alerts drivers to a cyclist’s presence.
Are reflectors required on bicycles?
No, reflectors are not required on all bicycles if local laws do not mandate them, but in many regions—including the U.S., EU, and Japan—they are legally required for bikes ridden at night. Regulations typically specify a white front reflector, red rear reflector, amber pedal reflectors, and wheel or side reflectors to ensure 360-degree visibility. Related terms include traffic law compliance, retroreflection, visibility standards, and road safety equipment. The value is that even when not legally required, reflectors serve as a passive, maintenance-free safety measure that improves rider visibility to motorists.
What reflectors are required on bicycles?
The reflectors required on bicycles typically include a white front reflector, red rear reflector, amber pedal reflectors, and amber or white wheel/side reflectors, because these placements provide 360-degree visibility and comply with most traffic safety regulations worldwide. These reflectors ensure that a cyclist is visible to motorists from the front, rear, and sides, especially in low-light conditions. Related terms include retroreflective surfaces, safety compliance, visibility standards, and passive lighting systems.
Are bicycle reflectors required by law in California?
No, bicycle reflectors are not optional in California if you ride at night, because California law (CVC §21201) requires them for visibility and safety. But during daytime riding, they are not legally required. The law specifies a white front reflector or light, red rear reflector or light, amber or white pedal reflectors, and white or amber wheel/side reflectors. Related terms include California Vehicle Code, retroreflectors, nighttime cycling safety, and legal compliance. The value is that these requirements ensure cyclists are visible from all directions, reducing accident risks in low-light traffic.
How do you install a bike reflector?
You install a bike reflector by aligning it with the mounting bracket or bolt holes on the frame (front, rear, or seat post), then tightening it with a screwdriver or Allen key until secure. Proper installation ensures the reflector points directly forward or backward for maximum retroreflection. Related terms: mounting hardware, seat post clamp, bolt spacing, safety compliance.
How do you install bicycle reflectors in spokes?
You install bicycle reflectors in spokes by clipping or sliding the reflector onto the spokes and tightening the integrated clamp or screw so it stays in place. The reflector should sit centrally and evenly to prevent wheel imbalance. Related terms: spoke-mounted reflector, rotational visibility, wheel balance.
How do you remove bicycle wheel reflectors?
You remove bicycle wheel reflectors by loosening the small screw or clip that holds them to the spokes, then sliding them off carefully. Some are snap-fit designs, so gentle prying with a flathead screwdriver may be needed. Related terms: spoke clamp, reflector removal, wheel maintenance.
How do you fix a bicycle reflector pedal that broke off?
You fix a bicycle reflector pedal that broke off by either replacing it with a new pedal reflector insert (if compatible) or using adhesive-backed reflective stickers or aftermarket clip-on reflectors if the original cannot be repaired. This restores the legally required amber pedal visibility. Related terms: pedal reflector insert, clip-on reflectors, adhesive reflective tape, legal compliance.
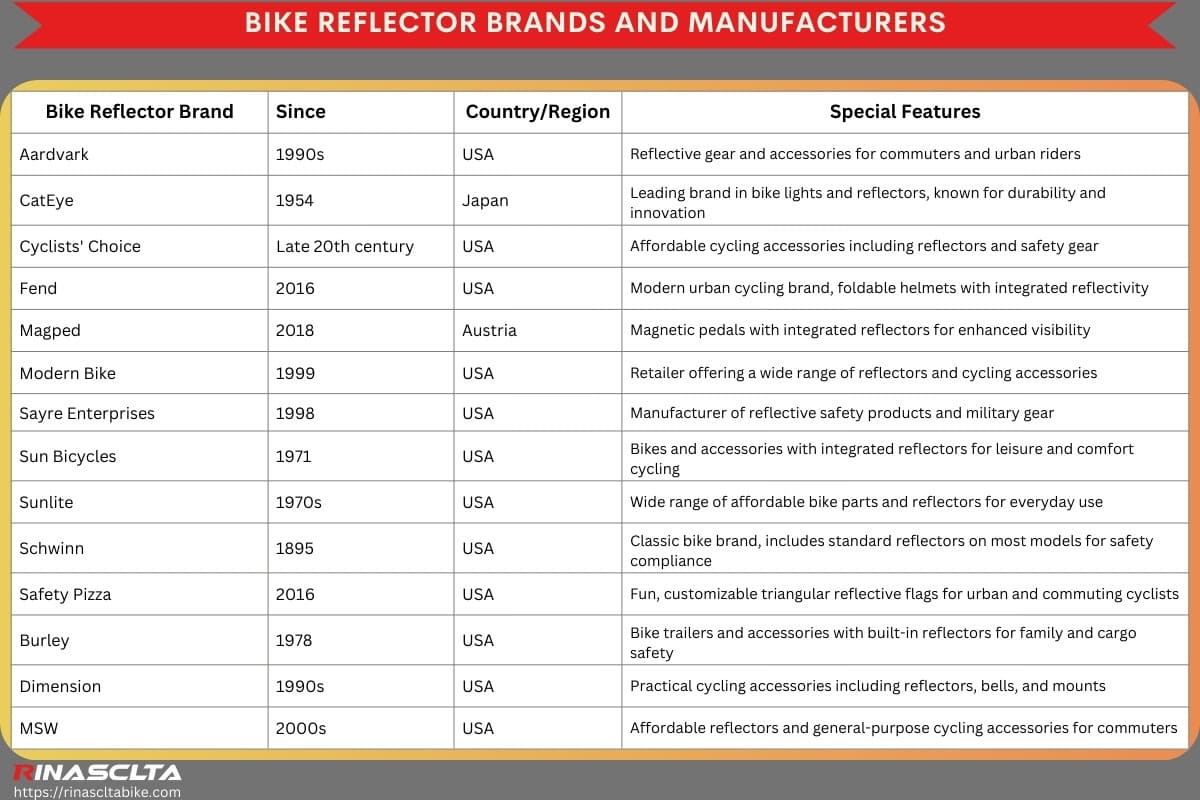
Bike reflector brands and manufacturers
Bike reflector brands and manufacturers are a vital part of the cycling safety industry, producing accessories that enhance visibility and help riders comply with traffic laws. From long-established companies like CatEye and Schwinn, which have decades of experience in reflector and lighting technology, to innovative newcomers like Fend and Safety Pizza, the industry blends tradition with modern design. Many brands also offer broader cycling products such as lighting systems, pedals, and helmets, with reflectors integrated into their safety ranges. Choosing a reputable brand ensures durability, compliance, and reliable visibility, giving cyclists confidence on the road.
| Bike Reflector Brand | Since | Country/Region | Special Features |
| Aardvark | 1990s | USA | Reflective gear and accessories for commuters and urban riders |
| CatEye | 1954 | Japan | Leading brand in bike lights and reflectors, known for durability and innovation |
| Cyclists’ Choice | Late 20th century | USA | Affordable cycling accessories including reflectors and safety gear |
| Fend | 2016 | USA | Modern urban cycling brand, foldable helmets with integrated reflectivity |
| Magped | 2018 | Austria | Magnetic pedals with integrated reflectors for enhanced visibility |
| Modern Bike | 1999 | USA | Retailer offering a wide range of reflectors and cycling accessories |
| Sayre Enterprises | 1998 | USA | Manufacturer of reflective safety products and military gear |
| Sun Bicycles | 1971 | USA | Bikes and accessories with integrated reflectors for leisure and comfort cycling |
| Sunlite | 1970s | USA | Wide range of affordable bike parts and reflectors for everyday use |
| Schwinn | 1895 | USA | Classic bike brand, includes standard reflectors on most models for safety compliance |
| Safety Pizza | 2016 | USA | Fun, customizable triangular reflective flags for urban and commuting cyclists |
| Burley | 1978 | USA | Bike trailers and accessories with built-in reflectors for family and cargo safety |
| Dimension | 1990s | USA | Practical cycling accessories including reflectors, bells, and mounts |
| MSW | 2000s | USA | Affordable reflectors and general-purpose cycling accessories for commuters |